Printing, packaging, electronics, and coatings, speed and efficiency are everything in the world. UV curing technology is such an important transformation of how inks, adhesives, and coatings are cured. But how does UV curing work? what makes it different, and why industries are rapidly adopting it. Let’s dive into this.
What is UV Curing?
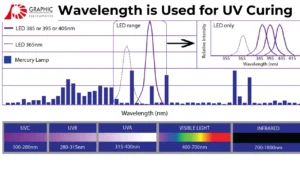
UV curing (Ultraviolet curing) is a photochemical process that uses ultraviolet light to instantly dry or harden materials such as inks, coatings, adhesives, and varnishes. Instead of waiting for solvents to evaporate like in traditional drying methods, UV curing solidifies the material within seconds — saving time, energy, and space.
How does UV Curing Work
UV curing works based on a chemical reaction called polymerization. UV-reactive materials (inks, coatings, adhesives) are applied to a surface. These materials contain photoinitiators – special chemicals sensitive to UV light. When exposed to UV light, these photoinitiators absorb the light energy and release free radicals. The free radicals trigger polymerization – a rapid chemical reaction that transforms the liquid layer into a hard, durable, and dry finish.
This entire reaction takes place in a fraction of a second, making UV curing one of the fastest drying technologies available.
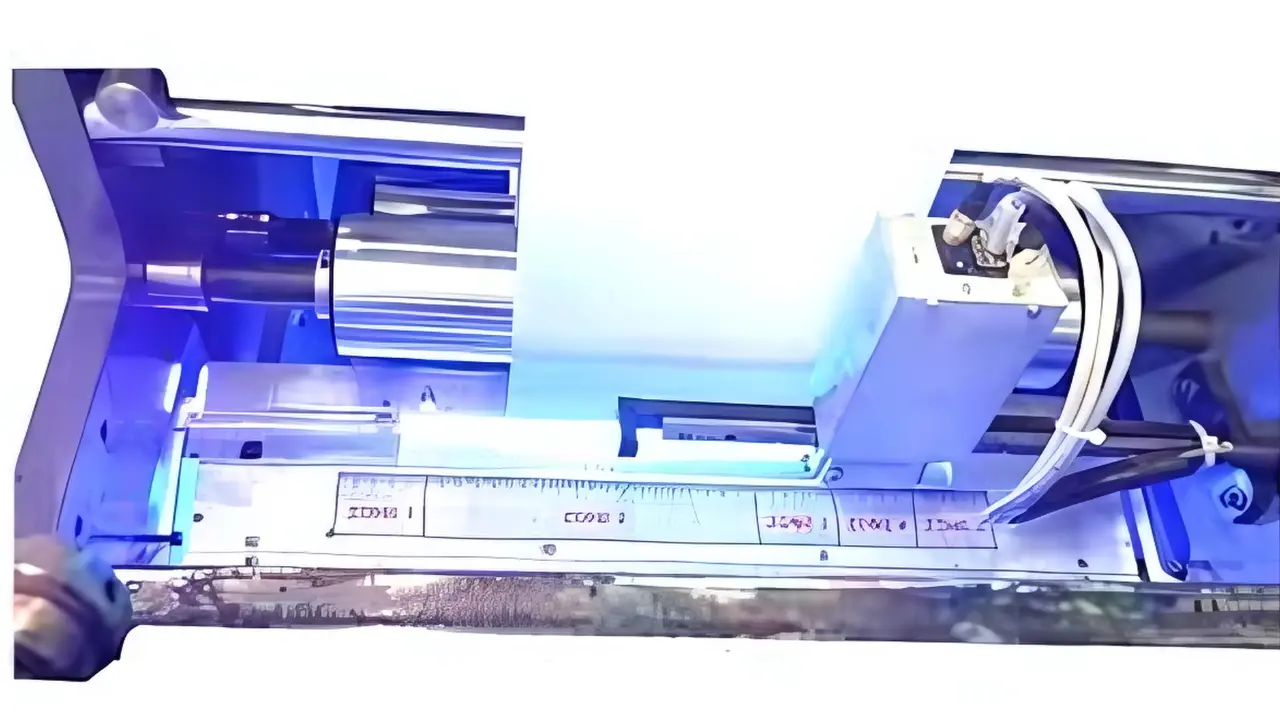
Components of a UV Curing System
A standard UV curing machine includes UV Lamp or UV LED source ( This is the heart of the system, emitting the ultraviolet energy needed to initiate the reaction), Reflectors( Enhance the efficiency of the UV light by focusing it on the coated surface) ,Cooling system( Keeps the machine and components at a safe operating temperature), Control panel(Allows precise control over exposure time, intensity, and other variables.)
Where is UV Curing Used?
UV curing is widely used across industries:
- Printing Industry: UV inks on paper, plastic, or metal dry instantly, making them perfect for high-speed print lines.
- Wood Finishing: UV-curable wood coatings offer a smooth, durable finish with no drying time.
- Electronics: UV adhesives are used to assemble components with precision and minimal downtime.
- Automotive: UV-cured clear coats provide scratch resistance and fast processing.
Why Choose UV Curing?
Here are some compelling reasons why to choose UV curing: it is used for Instant Curing, Energy Efficient, No Solvent Emissions, Compact Equipment, High Throughput.
So, how does UV curing work? In simple terms, it replaces time and heat with light and chemistry. It’s fast, clean, and reliable – everything modern manufacturing needs. Pramod Graphics Instrument Pvt. Ltd. understands the science and engineering that go into effective UV curing. Whether you’re in printing, packaging, or coatings, we offer custom UV curing systems designed for precision, performance, and productivity.