Ultraviolet (UV) light is used in many industrial applications, it is used especially in the fields of UV curing, printing, coating, and electronics manufacturing. Pramod Graphics Instrument Pvt. Ltd. understands how important it is to harness UV technology effectively — and at the heart of this technology lies a key factor: the wavelength of UV light.
Also Read : Silk Screen Printing Machine
What is UV Light?
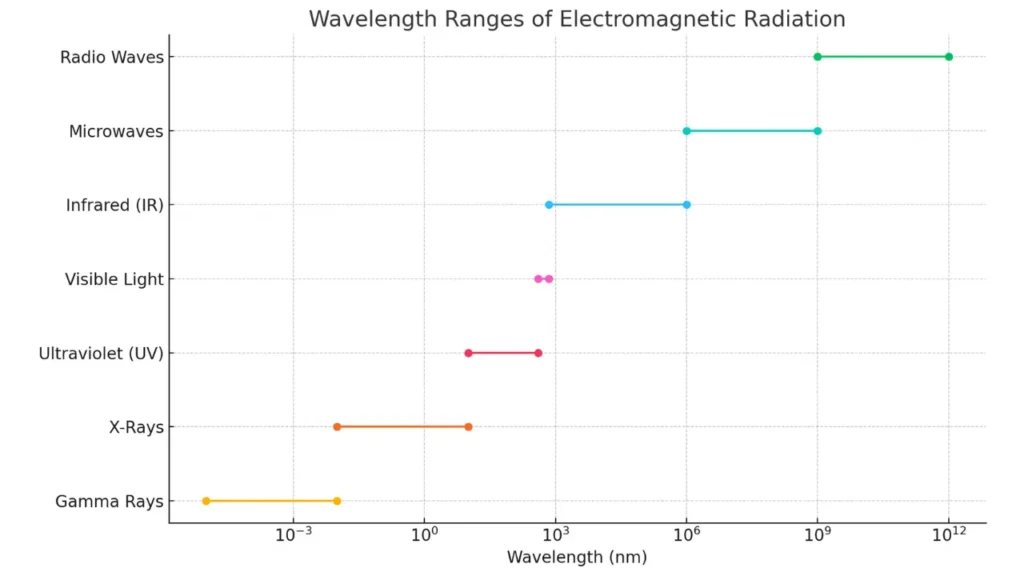
UV light is a type of electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than visible light but longer than X-rays. It falls in the range between 10 nanometers (nm) and 400 nanometers, and is divided into several categories based on wavelength:
- UV-A (315–400 nm) – Long-wave UV; commonly used in printing and curing processes
- UV-B (280–315 nm) – Medium-wave UV; less common in industrial use
- UV-C (100–280 nm) – Short-wave UV; primarily used for disinfection and germicidal applications
- Vacuum UV (10–200 nm) – Used in highly specialized environments
Wavelength Ranges Chart
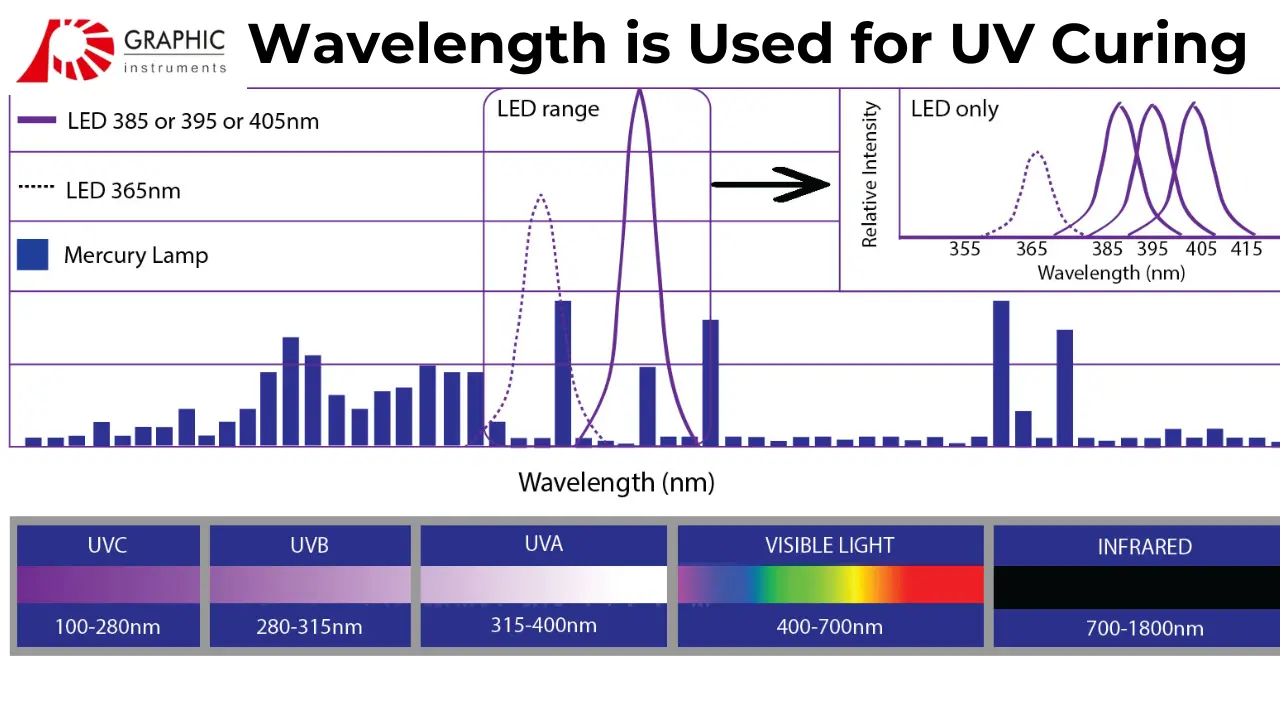
Why Wavelength Matters in UV Curing?
The effectiveness of UV curing systems — such as those found in our high-performance printing equipment — depends heavily on the specific wavelength of UV light being used. Here’s why:
Material Sensitivity: Different inks, coatings, and adhesives are formulated to respond to certain UV wavelengths. Using the wrong wavelength can lead to incomplete curing or damage to the material.
Curing Speed: The right wavelength ensures fast and thorough curing, improving production speed and product quality.
Energy Efficiency: Optimized wavelengths reduce energy consumption and prevent overheating or substrate warping.
Ideal Wavelengths for Industrial UV Applications
Most industrial UV curing systems operate in the UV-A range — typically around 365 nm to 405 nm. This range is safe for most materials and provides a balance of energy and penetration depth for reliable curing.
In certain high-performance applications, UV-C light around 254 nm may be used for precision curing or sterilization, but this requires careful handling due to its intensity and potential material sensitivity.
About Pramod Graphics Instrument Pvt. Ltd.
Pramod Graphics Instrument Pvt. Ltd. incorporate advanced UV curing systems into our machinery, engineered to deliver consistent performance with the ideal UV wavelength for your specific application. Whether you’re in packaging, labeling, electronics, or industrial printing, our expertise ensures that you get the most effective and efficient UV solution for your production needs.
Conclusion
The wavelength of UV light is more than just a scientific detail — it’s a critical factor in determining the success and quality of UV-based industrial processes. By understanding and using the correct wavelength, manufacturers can achieve faster production times, better material compatibility, and superior results.